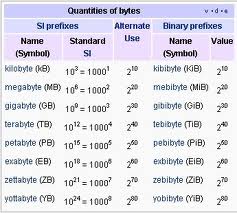
This chapter was very helpful in explaining a lot of the technical terms you hear but don’t always know what they mean. Have you ever heard of kilobytes, megabytes, or gigabytes? These prefixes, similar to other units of measure, talk about bytes in large quantities. Why would we need such large quantities of bytes? Take a CD for example, it can hold 650 megabytes. Everyone from large corporations to yourself could need the extra space when you consider music and digital files.
Plug-ins and extensions are software that allows the user to do more than just see the display, some are ad blockers, translators, etc.
HTML is a markup language that shows the browser how to display the page with all its texts, graphics, images, etc. When a Web page displays a copy of the HTML document saves on the computer. The code then tells the computer how to build the page. There are online services and software that can help you create a page but it is important to know how to do HTML for your own benefit. HTML uses opening and closing tags to create a pair. A pair designates a paragraph, bolded word, headline, boxes or bullets. You can use HTML in image tags to create alternate text, a border, show width or height, alignment, etc.
CSS (cascading style sheets) is another markup language that can add a bit more creativity into the Web page, unlike HTML. You can edit, modify and troubleshoot existing Web pages and designs. In CSS you declare a font, color, size and other attributes for a specific type of content. XML works with HTML, is customizable and describes what data is. It is most often used in RSS feeds.
Some Helpful Definitions:
• Byte– unit of measure for digital information; contains eight consecutive bits and is capable of storing a single ASCII (“as-kee”; American Standard Code for Information Interchange) character.
• Internet – system of computer networks that allows users to connect by using the Internet Protocol Suite (TCP/IP) and includes email, instant messaging and file transfer (FTP).
• The Web – refers to a way of accessing information through the network, using hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP) and web browsers. It doesn’t include email, instant messaging and file transfer (FTP).
• Web server – a special type of computer that stores and distributes information over the Internet.
•URL (uniform resource locator) – also known as a “Web address”. Computers recognize the Web address’ corresponding IP address when you type it into the Web browser.
• IP address (Internet Protocol) – a unique, numeric identity of a Web address.
• Domain name – secures a human-readable Web address and associates it with an IP address.
• Web browsers – tools that people use to access the Internet that is part of the World Wide Web. They do three things:
1. It searches and finds information on Web servers.
2. It retrieves the information and brings it back to you.
3. It renders the information for display on your computer or mobile device.
• Cache – temporary storage of all the files you download while you’re browsing the web.
• RSS (Really Simple Syndication) – subscribes to an information feed that gets delivered directly to an RSS reader or Web browser. This is a great tool for sifting through lots of information and keeping updated on different feeds.
• FTP (File Transfer Protocol) – simply moves a file from one computer to another.
To break it up, here is a video that describes some of my sentiments toward technology.
1 comment so far ↓
There are no comments yet...Kick things off by filling out the form below..